Ruth Waddell Smith

Research
Forensic Chemistry
(Research Description PDF)
Research in our group focuses on improving current methods for the analysis, characterization, and identification of forensic evidence, while ensuring that such methods are directly implementable in forensic laboratories. Much of our research also includes application of multivariate statistical procedures for the association and discrimination of various types of forensic evidence. Our current main areas of interest are in developing a kinetic model to predict evaporation of ignitable liquids for fire debris applications and in developing a method to statistically compare mass spectral data for seized drug identification.
Fire Debris Analysis
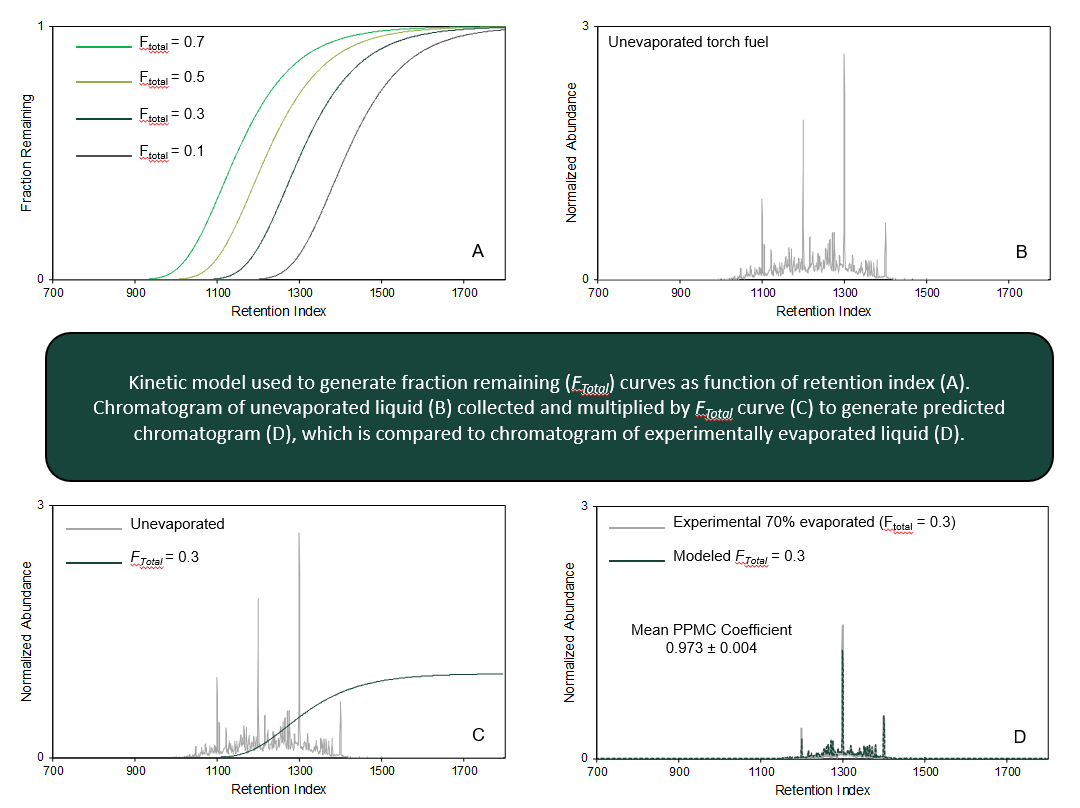
Our research is focused on the development, refinement, and application of a model that can be used to generate the chromatogram corresponding to any evaporation level of an ignitable liquid. The model is based on first-order kinetics and is used to predict evaporation rate constants of compounds as a function of retention index. These predicted chromatograms can then be used to populate reference collections, eliminating the need to experimentally evaporate liquids. Current work focuses on (1) refining the model to improve prediction of more volatile compounds that are present in gasoline, which is the most commonly identified liquid in fire debris samples, (2) demonstrating broader applicability of the model to predict evaporation of liquids of different chemical classes, and (3) in collaboration with Prof. Glen Jackson at West Virginia University, investigating the effect of elevated temperature on the predictive abilities of the model. This work is currently funded by the National Institute of Justice (Award No. 2018-DU-BX-0225).
Controlled Substances
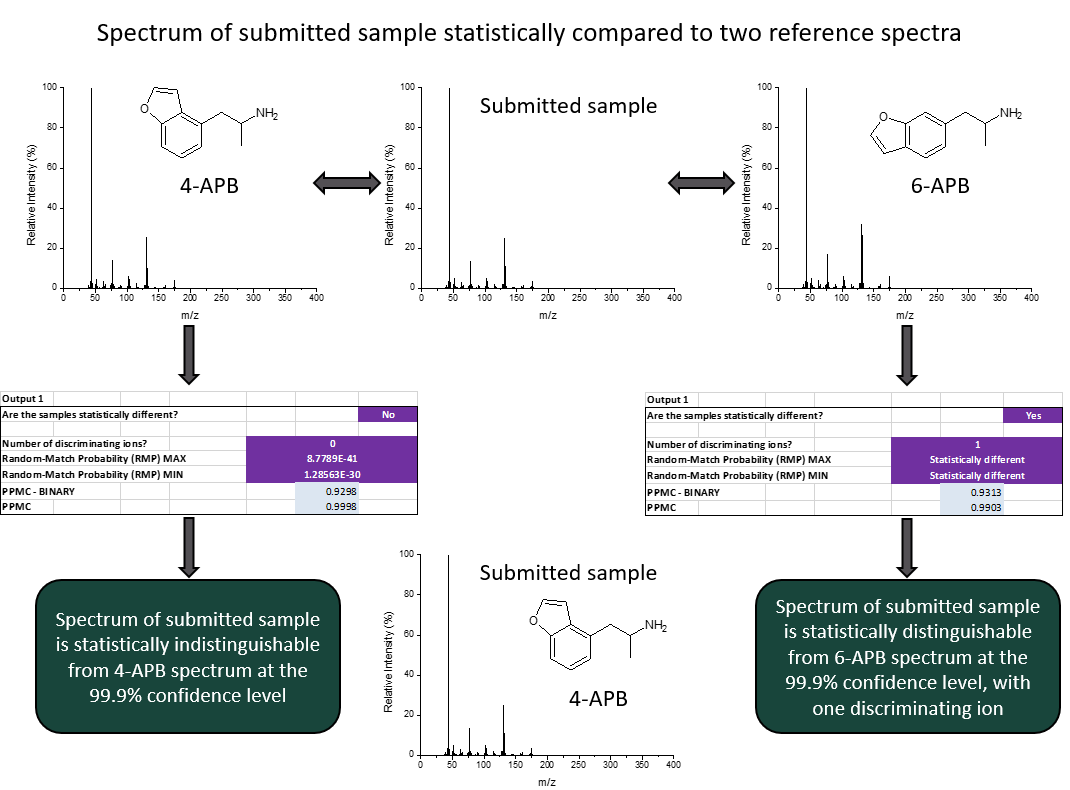
Our work in this area is focused on developing tools to aid in the characterization and identification of novel psychoactive substances (NPS). We have developed a method for statistical comparison of mass spectra and are currently testing the method for the differentiation of positional isomers of ethylmethcathinone, fluormethamphetamine, and fentanyl analogs. In this area, we are interested in determining the significance of discriminating ions based on fragmentation mechanisms. We have also demonstrated application of multivariate statistical models to classify various NPS according to structural subclass and are continuing this work to focus on fentanyl analogs.
Contact / Webpage
Area(s) of Interest
Forensic (F)
Analytical (An)
Selected Publications
Improvements in a Kinetic-Based Model to Predict Evaporation of Gasoline, Eklund, N.K., Capistran, B.A., McGuffin, V.L., & Waddell Smith, Forensic Chemistry 2020, 17, 100194.
Statistical Comparison of Mass Spectra if Salvinorins in Salvia Divinorum and Related Salvia Species, Bodnar Willard, M.A., Hurd, J.E., Waddell Smith, R., & McGuffin, V.L., Forensic Chemistry 2020, 17, 100192.
Comparison of Variable Selection Methods prior to Linear Discriminant Analysis Classification of Synthetic Phenethylamines and Tryptamines, Setser, A.L. & Waddell Smith, R., Forensic Chemistry 2018, 11, 77-86.
Fixed- and Variable-Temperature Models to Predict Evaporation of Petroleum Distillates for Fire Debris Applications, McIlroy, J.W., Waddell Smith, R., & McGuffin, V.L., Separations 2018 5(4), 47.
Characterization of 2C-Phenethylamines Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Kendrick Mass Defect Filters, Anstett, A., Chu, F., Alonso, D.E., & Waddell Smith, R., Forensic Chemistry 2018, 7, 47-55.
Statistical Comparison of Mass Spectra for Identification of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants, Bodnar-Willard, M.A., McGuffin, V.L., & Waddell Smith, R., Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 270, 111-120.
Mathematically Modeling Chromatograms of Evaporated Ignitable Liquids for Fire Debris Applications, Waddell Smith, R., Brehe, R.J., McIlroy, J.W., McGuffin, V.L., Forensic Chem. 2016, 2, 37-45.
CV
B.S. 1999, Univ. of Strathclyde (Scotland)
Ph.D. 2003, Univ. of Strathclyde (Scotland)